Welding is a hazardous activity to which millions of workers are exposed every year. Responsibility for Health and the safe work procedure is our responsibility. So that, all the workmen can return to their home same as they arrived at work.
Weldin safety measures always need to design in such a way that it protects all employees, Properties of the company, and increases the productivity of welders. Proper training, regular inspection of welding equipment, and ensuring worker’s condition are some of the most important ways.
In this article, we got to know the hazards and safety precautions during welding with other useful information like:
- Types of welding according OSHA.
- Why health and safety is important to lookout during welding.
- Different types of hazards and its risks during welding.
- What precautions we need to take during confined space welding?
- General welding safety checklists and steps to create better environment for welding.
More to Read: What is Orbital Welding? Benefits, Factor affecting, Application, Advantages, Disadvantages
Table of Contents
Types of Welding
As per OSHA classification, welding is divided into 02 groups: A) Fusion (only heat application) and B) Pressure ( Heat and pressure application) to join two weld metals together. OSHA further divides fusion welding into 03 categories:
- Electric Arc Welding: Welding process where electricity is applied to generate heat to melt base metal and filler. this is further divided into 04 types according to amount of fue production during welding (listed from leat to most):
- Flux core Arc welding (FCAW)
- Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW)
- Gas metal arc welding (GMAW) or Metal inert gas welding (MIG)
- Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) or Tungsten inert gas welding (TIG)
- Gas Welding: Use of flames of burning gas normally acetylene is used to melt the base metal at the point of joint.
- Thermit: Use of chemical reaction to produce intense heat instead of gas fuel or electric current.
More Resources: Types of Pipe Connection: Welded, Bolted, Threaded, Grooved
Importance of Health and Safety during Welding
Controlling the safety of workers may seem like no thoughtful effort but in reality, there is a lot to consider. From fumes to tools, everything leaves its impact during welding work. If welders are working at height or in some non-familiar and high-risk environment (e.g. Offshore project or Electric plant) then safety concerns increase a lot.
All the standards and considerations must be practiced and in line with the Health and Safety at work Act 1974. These acts make it the duty of an employer to ensure the health, safety, and welfare of all the workers at work. This also instructs to provide training, PPE, and supervision to workers. Maintenance of all types of machinery is also included in this act.
Safety precaution during welding not only takes care of the health and safety of the welder and worker but also ensures that as a company you won’t have to suffer profit loss because of any legal consequences. Human life is priceless but you can put some money to save it.
More Resources: Piping Supports: Types, Codes, Design, Selection, Working, Installation
Hazards and Risks during Welding
Welding operation carries several types of hazards with itself for the welder as well as whoever is in the vicinity. It is our responsibility to know about any kind of risks and hazards that can be present in welding locations. This is a must to understand and identify the hazards, their risk, and level of severity.
Welding operations present several hazards to both those undertaking the activity and others in the vicinity. Therefore, it’s important that you are aware of the risks and hazards welding poses, and understand what precautions you can take to protect yourself. There are many types of hazards during welding operation as follows:
Electric Shock
During Arc welding, live electric current is always present in electrical circuits of the welding machines to create heat and melt metal. This creates a hazard of electric shock during welding which is the most serious hazard possessed by the welding operation. You are also always at risk of secondary electric shock if some part of the welding holder or electrode circuit touches you during welding.
In most cases, you risk yourself with these hazardous conditions when:
- You work in wet or moist condition.
- If working with wet cloths.
- working on metal floor or structure
- When in posed in some restricted position like lie, kneel or crouched.
- If you welding machine i=body earthing is not connected.
You are particularly at risk if you work in electrically hazardous conditions. These include welding:
- In damp conditions.
- While wearing wet clothing.
- On metal flooring or structures.
- In cramped conditions where you are required to lie, kneel or crouch.
Noise Hazards
When welding activities are in progress, you are exposed to loud sounds and prolonged noises. Noise is called Loud when it exceeds 85 dB (decibel). Welding activities like flame-cutting, arc welding can produce a level of noise over 100 dB. This can be dangerous to the ears can result in permanent hearing loss.
Hearing loss because of Noise can have the following side effects:
- Always feeling some kind of ringing sound in the ear. This is known as tinnitus.
- Feeling some occasional dizziness, called as vertigo.
- Increase in heart rate.
- Abnormal increase in blood pressure.
- Always having some amout of headache.
Exposure of Ultraviolet (UV) and Infrared (IR) radiation
During welding, this emitted intense UV light, without appropriate PPE and welding glasses it can be harmful and painful. Sometimes this also generates a long-lasting painful condition called Arc-eye. There are some other factors that affect the severity of injury such as:
- Distance
- Duration
- Angle of penetration
Long-term exposure to arc flash can also lead to cataracts and loss of vision. Some other reasons for eye damages are:
- Inclusion of foreign particle in the eyes like arc spatter, debris, grits and dust.
- long time direct contact with fumes and gases in eyes.
Exposure in Fumes and Gases
During welding activity, there are always invisible or visible gaseous fumes present including, Ozone, Nitrous oxide, Chromium or Nickel Oxide, and carbon monoxide. These gases are easy to get dissolved in the human lungs. Depends on the type of gas, its concentration, and duration of exposure this can result in severe damage.
Long time exposure with gases, welder and employees in the vicinity can be affected from following diseases:
- Pneumonia. Regular exposure to welding fumes and gases can result in a lung infection which could then develop into pneumonia. While antibiotics can usually stop the infection, severe pneumonia can result in hospitalisation, serious illness and fatalities.
- Occupational asthma. Chromium oxides and nickel oxides produced by stainless steel and high nickel alloy welding can both cause asthma.
- Cancer. All welding fumes are internationally considered ‘carcinogenic’.
- Metal fume fever. Welding or hot work on galvanised metal and high steel weld fume exposure can often result in ‘flu-like’ symptoms, which are usually worse at the start of the working week. You might have heard that drinking milk before welding will help you avoid developing metal fume fever, but this is a myth.
- Throat and lung irritation, including throat dryness, tickling of the throat, coughing and tight chests.
Burns
The combination of heat, UV rays, and IR rays can result in severe burns. Welding is a high-temperature operation that can affect skin or eyes. these burns can be very serious and also happen very quickly.
Welding burn normally occurs while welder shows some carelessness and thinks of escaping precautions for some quick welding. This is bad welding practice and should never allow even for some time.
Fire and Explosion
Fire and explosions happen because hot work has taken many lives. Hot metal parts, sparks, and drops of molten metal can easily start a fire. Before starting welding works you should always look out for:
- Any kind of flammable material nearby.
- Proper use of fire retardent cloth to cover welding work zone.
- Availablty of fire-extinguisher nearby welding job.
- Removal of any kind drum that may contain (even in small amount) oil, paint, spirits etc.
Hazards of Welding in Confined Space
A confined space is a place with a limited access point with no airflow and ventilation. Adequate ventilation and airflow regulation is the most important thing during work in confined space. In confined space, the dangerous concentration of toxic fumes and gases is easy to accumulate because of the small space that can make a person unconscious or even death because of suffocation.
Continuous welding process in confined space displaces oxygen available in the air and generates toxic fumes and gases like CO. These gases are much dangerous to health and even high concentration of some fumes can lead to explosion too.
All welders who enter in confined space either on regular basis or for some emergency situation must follow the following precaution for their safety:
- All welder must be equipped with safety harness, Lifeline, appropriate protective clothing, and self-contained breathing apparatus. Never use any air purifying respirator as it can create suffocation in confined space.
- Gas cylinder and welding power connection source should be located in secure location outside of confined space.
- Confined space should be test for availablity of toxic, flammable or explosive gas via gas detector before entering.
- A well trained welding helper must stay always outside the confined space with fire extinguisher and PPE.
- Only air ventilation should be use. Never use oxygen for ventilation.
- Use countinuous ventillation when welding is in progress.
- Anything unneccessary other than welding equipment and necessary protective gear should be removed from confined space.
More Resources: SOP for jacketed piping: Types, General requirement, Fabrication, Erection, Testing
Welding safety precautions and Tips
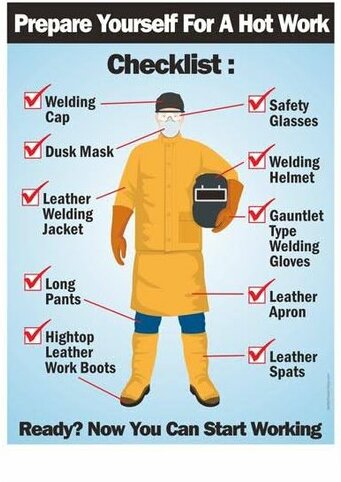
Welding safety precautions are actionable steps that should be taken by welders to prevent welding-related incidents and injuries such as burns, fire, explosion, electrocution, or suffocation. In order to eliminate or reduce the welding hazards, welders should practice the following safety precautions and tips accordingly:
- Always use proper ventilation and local exhaust of fumes and gases from welding zone.
- Report any concerns and welding related hazards immiditely to supervisors.
- Fire and electric resistance cloths, face shield, hand gloves, aprons and boots must to use.
- Earmuff or earplug always be used according to noise level of vicinity.
- Always keep a suitable class of fire extinguisher while doing welding. Make sure fire extinguisher gauge is full.
- No flammable material should be there nearby welding zone.
- Always use fire retardent cloth of resist hot metal droplets and spark.
- Always use inspect welding tools and machineries. Before use check for any faulty wire and welding holders on daily basis.
- Proper use of IR and UV filter glasses to save your eye.
- Don’t leave workplace instanly after welding job completion. Stay some time there untill welding metal get cold.
General Safety check list for welding
Every Welding job should be pre-planned and safety arrangements should be done accordingly. Before starting of welding job there are a few things that should be verified. This safety checklist for welding will useful before commencing the welding job. This Checklist is divided into 04 parts i.e.
- General Information
- Pre-operation information
- On-going work information
- Post-operation information
General Information
- Description of welding job should be recorded
- Location of welding work should be verified
- Type of welding should be verified
Pre-operation welding work Information
This information should be recorded in 03 stages:
Welder’s Information
- Are all welders well qualified and trained?
- Are all instruction clear and understood by welders?
- Are all welders familiar with the welding machine they are going to use?
- Are all welders familiar with the type of metal to weld?
- Do all welder wear all required PPEs?
- Are welders aware of safety protocol during emergency?
Welding Machine
- Are all welding cable, wiring, electrod holders are insulated and in good condition?
- Is welding machine properly inspected and certified for use?
- Are all welding terminal and joint in good condition?
- Is the size of cable suitable for voltage application?
- Is body earthing wire is properly connected?
Work Area
- Is work area clean and free from flammable materials?
- Is ventillation is applicable for work area?
- Is there suitable class of fire extinguisher available nearby?
- Are combustible wetted or protected?
- Is cumbustible walls shielded or guarded?
- Is fire blanket available in work location?
- Are warning sign placed in work location?
- Is work area restricted for other workers?
On-going welding work information
- Is arch shield used to provide extra layer of protection?
- Does respirator required for welders?
- Are all welding machine insulated from work and ground?
- Are all welders use dry and fire retardent cloths?
- Does welding operator avoid coiling of welding filler wire around their body?
- Is pressurised cylinder handle carefully?
- Are valve cylinders placed with valve end up?
- Does cylinder attached when lifting welding machine to welding location?
Post-operationwelding work Information
- Are all electrode bits swept away from welding location?
- Are all welding equipment turned off and stored in proper location?
- Are gas cylinder valve closed and put away safely?
- Are any other waste of welding process disposed properly in designated area?
- Are all incident and welding work status reported to superviser?
- Are all weld job attained its normal environment temperature?
- Is it safe to leave work location after welding?
More resources: What Is RF Pad? How To Calculate Reinforcement pad dimensions?
05 Steps to create a safer Welding Environment
There is always some space for improvement even in the most perfect system. In case of making a healthy and safer welding environment, we can follow 05 simple steps for making it safer for the employees and employer.
- Elimination of Hazard: Its the most effective way for mitigation of a hazard entirely. But Welding is a job that carries hazard with its process on its own Like fumes, heat, radiation. For e.g. A faulty welding machine need to repair or replace with well inspected welding machine for safer welding.
- Substitution: When elemination something is not so pratical. We need find some ulternate ways to make the working environment safer. Substitution doesn’t eliminate the risk completely but this reduce its severity. For e.g. Welding with E6011 can replaced with E7018 so less fumes can be there.
- Engineering control: When Substitution doesn’t make its effective role. Engineering controls comes in action. Yet engineering control can’t get rid of the hazards and its risks completely but this can isolate people from hazard. For e.g. In confined space welding Local ventilation is the only engineering control that can stop welder from suffocation.
- Administrative control: This kind of control relates to the procedure and norms by which any person conducts their work. Norms and procedure are made for effective implement of safety norms but this need to change according to place, environement, and working conditions. For e.g. In case of boiler tube welding, Helmet of welder create an obstacle during welding and that can be replace with welding google.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): PPEs are final control and should always worn by every employee during working hours. This is the physical barries between human body and hazard. Yet this is least effective way of protection from hazard but it play a vital from many types of injuries. For e.g. Helmet is necessary when you work in construction fields as it save your head from injuries.
Conclusion
Ensuring welding operation safety is all about preparation. No employee or worker should ever start welding work without the correct welding machinery, information, and training. Every new environment and situation needs a separate assessment of hazards and risks according to which new safety measures are introduced.
Hazards of welding may change with new technologies. Wherever hot work is going on there is always a risk of fire and explosion. we must inspect the condition closely before starting welding and after finish also need to check for the conditions after welding.
It is important for welders, supervisors, and safety professionals to continuously follow the hierarchy of control to guard against traditional know welding hazards. To keep every worker safe from any kind of known risk and secure properties from any damage.




