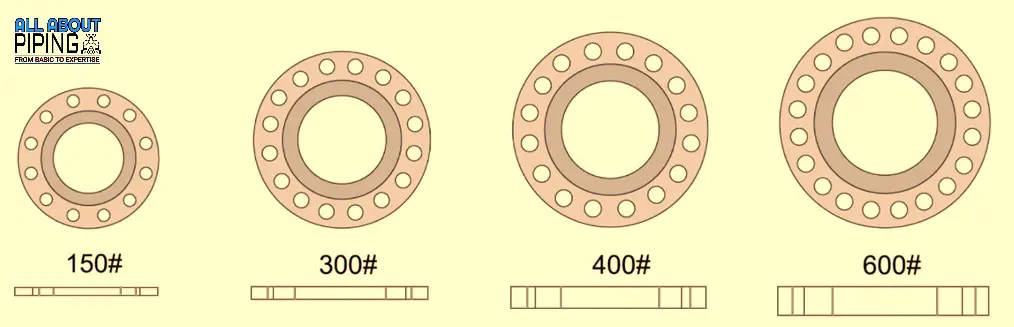
In piping, flange connections are too common but even with the same nominal size of the flange, there is a variety of flange in terms of flange class. Different piping systems having different working conditions, and we can not use the same type of flange in every location.
Flange pressure rating system is introduced in Piping to provide uniqueness towards the use of flange according to pressure and temperature of the piping system. A higher class of flange will have more capacity than that of the lower class of flange with the same nominal size.
In this article we will know in detail about:
- What is flange pressure rating and why it is necesseary?
- Flange pressure rating designations and Its types.
- Pressure-temperature charts for different material types.
- Selection method of flange for a specific piping system and formula for flange rating.
- Effect of flange pressure rating on size of flange.
More to Read: What is Cryogenic Piping? A brief on Piping material, Insulation, Pipe Sizing, and Hazards.
Table of Contents
What is Flange pressure Rating?
Every pipe fitting has some pressure holding capacity which is derived according to its metal type and thickness. A flange is among the main components of pipe that connect with valves, Equipment, and other piping spools and hold pressure developed in the piping system during the process.
Flange Pressure Rating is the identification of a specific designation that indicates how much pressure that flange can hold till what maximum temperature. In Simple Words, ” Flange Pressure Rating or Class indicates the maximum pressure a flange can withstand with rising temperature up to a limit for a specific temperature range.“
A flange with a higher rating or class is stronger than a flange with a lower rating or class at some specific temperature criteria. Higher rating flanges can withstand higher pressure in higher temperatures provided they are made of the same material. Flange made of different material shows different pressure and temperature holding capacity at same rating and class of flange.
More Resources: Types of Pipe Connection: Welded, Bolted, Threaded, Grooved
Why Flange pressure rating is required?
While designing a piping system for processing some fluid, there are calculations of getting maximum pressure and temperature during the process. Welding joints with properly analyzed pipe thickness is assured to hold these variables, So maximum chances of leakage of fluid is possibly from the flange joint.
To stop those flange leakage, the Flange joint and hence flanges must be so efficient to hold the operating pressure and temperature of the process. Flange pressure rating is required to fulfill 03 most important purpose for selection of flange:
- Standardrising the flange dimensions all over the world.
- Selecting an efficient flange with lowest cost possible.
- Reducing unwanted weight from piping system because of flange metal.
Pressure Rating Designation of Flanges
Flange pressure ratings are indicated in Class, Lb, or Pound. Class is followed by a dimensionless number is the designation of pressure-temperature rating of flanges. There is a total of 07 types of flange rating designations which are symboled with the “#” :
- 150#
- 300#
- 400#
- 600#
- 900#
- 1500#
- 2500#
A flange is designated with many indications like 150 Lb, 150 Lbs, 150#, and Class 150. All of these have the same meaning. But there is only one correct indication and that is ” Pressure class”.
Type of flange pressure rating
There are mainly 02 types of flange pressure-temperature rating standards that are commonly used in piping or pipeline project flange selection:
- Pressure-Temperature rating for API flanges: This is used for oil drilling and wellhead system application. Here API flanges are used which are based on API 6A standard. The pressure temperature rating have a range from 2000 psi to 20,000 psi.
- Pressure-Temperature rating for ASME or ANSI Flanges: For any other application except oil drilling and wellhead, ASME or ANSI flanges are used. ASME B16.5 are used up to 24″ Flange size and ASME B16.47 is used for flange above 24″ size.
Nominal Pressure Rating for flanges
Nominal Pressure or Pressure Nominal is a rating designator for flanges. This is followed by a designation number that indicated the approximate pressure it can withstand in bar. PN (Pressure nominal) is a European standard system.
The common pressure range designation used in the European standard system is PN2.5, PN6, PN10, PN16, PN25, PN40, PN63, PN100, PN160, PN250, PN320, PN400, and so on. For example, a PN16 flange is designed to withstand a maximum pressure of 16 bar of design pressure.
Conversion between Pressure class anf Nominal Pressure
As both of the systems for flange pressure rating, i.e. PN and LB are not so commonly interchangeable because of variation of different pressure ratings and holding capability of Nominal pressure. It will be better to show an approximate conversion table which is frequently used to show how the different pressure classes compare with each other. These conversions are not exact but are close enough for daily use purposes:
| Class | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
| PN | PN20 | PN50 | PN68 | PN110 | PN150 | PN260 | PN420 |
Flange Pressure Rating chart for Flange selection
Every metal shows different properties in different pressure and temperature range. And because of that reason flange made of different metals can withstand different pressure and temperature even of the same class. This Pressure-temperature chart below will help you to know which rating flange with which metal can hold the required pressure as per the piping system.
From the chart below you can easily find out if your system requirement matches with flange class or not. All values shown here are in psi (Pressure per Square inch) and as per ASME B16.34 standard for end connection types.
Pressure temperature rating chart for ASTM A105, A350 Gr. LF2 & LF6 Class 1
| Temperature (in F°) | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 100 | 285 | 740 | 985 | 1480 | 2220 | 3705 | 6170 |
| 200 | 260 | 680 | 905 | 1360 | 2035 | 3395 | 5655 |
| 300 | 230 | 655 | 870 | 1310 | 1965 | 3270 | 5450 |
| 400 | 200 | 635 | 845 | 1265 | 1900 | 3170 | 5280 |
| 500 | 170 | 605 | 805 | 1205 | 1810 | 3015 | 5025 |
| 600 | 140 | 570 | 755 | 1135 | 1705 | 2840 | 4730 |
| 650 | 125 | 550 | 730 | 1100 | 1650 | 2745 | 4575 |
| 700 | 110 | 530 | 710 | 1060 | 1590 | 2655 | 4425 |
| 750 | 95 | 505 | 675 | 1015 | 1520 | 2535 | 4230 |
| 800 | 80 | 410 | 550 | 825 | 1235 | 2055 | 3430 |
| 850 | 65 | 320 | 425 | 640 | 955 | 1595 | 2655 |
| 900 | 50 | 230 | 305 | 460 | 690 | 1150 | 1915 |
| 950 | 35 | 135 | 185 | 275 | 410 | 685 | 1145 |
| 1000 | 20 | 85 | 115 | 170 | 255 | 430 | 715 |
Pressure temperature rating chart for ASTM A350 Gr. LF3, A350 LF6, Class 2
| Temperature in °F | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -20 to 100 | 290 | 750 | 1000 | 1500 | 2250 | 3750 | 6250 |
| 200 | 260 | 750 | 1000 | 1500 | 2250 | 3750 | 6250 |
| 300 | 230 | 730 | 970 | 1455 | 2185 | 3640 | 6070 |
| 400 | 200 | 705 | 940 | 1410 | 2115 | 3530 | 5880 |
| 500 | 170 | 665 | 885 | 1330 | 1995 | 3325 | 5540 |
| 600 | 140 | 605 | 805 | 1210 | 1815 | 3025 | 5040 |
| 650 | 125 | 590 | 785 | 1175 | 1765 | 2940 | 4905 |
| 700 | 110 | 570 | 755 | 1135 | 1705 | 2840 | 4730 |
| 750 | 95 | 505 | 670 | 1010 | 1510 | 2520 | 4200 |
| 800 | 80 | 410 | 550 | 825 | 1235 | 2060 | 3430 |
| 850 | 65 | 270 | 355 | 535 | 805 | 1340 | 2230 |
| 900 | 50 | 170 | 230 | 345 | 515 | 860 | 1430 |
| 950 | 35 | 105 | 140 | 205 | 310 | 515 | 860 |
| 1000 | 20 | 50 | 70 | 105 | 155 | 260 | 430 |
Pressure temperature rating chart for ANSI FLANGE ASTM A350 Gr. LF1.csv
| Temperature °F | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -20 to 100 | 235 | 620 | 825 | 1235 | 1850 | 3085 | 1545 |
| 200 | 215 | 560 | 750 | 1125 | 1685 | 2810 | 4680 |
| 300 | 210 | 550 | 730 | 1095 | 1640 | 2735 | 4560 |
| 400 | 200 | 530 | 705 | 1060 | 1585 | 2645 | 4405 |
| 500 | 170 | 500 | 665 | 995 | 1495 | 2490 | 4150 |
| 600 | 140 | 455 | 610 | 915 | 1370 | 2285 | 3805 |
| 650 | 125 | 450 | 600 | 895 | 1345 | 2245 | 3740 |
| 700 | 110 | 450 | 600 | 895 | 1345 | 2245 | 3740 |
| 750 | 95 | 445 | 590 | 885 | 1325 | 2210 | 3685 |
| 800 | 80 | 370 | 495 | 740 | 1110 | 1850 | 3085 |
| 850 | 65 | 270 | 355 | 535 | 805 | 1340 | 2230 |
| 900 | 50 | 170 | 230 | 345 | 515 | 860 | 1430 |
| 950 | 35 | 105 | 140 | 205 | 310 | 515 | 860 |
| 1000 | 20 | 50 | 70 | 105 | 155 | 260 | 430 |
Pressure temperature rating chart for ASTM A182 Gr. F1 (Chrome Moly)
| Temperature °F | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -20 to 100 | 265 | 695 | 925 | 1390 | 2085 | 3470 | 5785 |
| 200 | 260 | 680 | 905 | 1360 | 2035 | 3395 | 5660 |
| 300 | 230 | 655 | 870 | 1305 | 1955 | 3260 | 5435 |
| 400 | 200 | 640 | 855 | 1280 | 1920 | 3200 | 5330 |
| 500 | 170 | 620 | 830 | 1245 | 1865 | 3105 | 5180 |
| 600 | 140 | 605 | 805 | 1210 | 1815 | 3025 | 5040 |
| 650 | 125 | 590 | 785 | 1175 | 1765 | 2940 | 4905 |
| 700 | 110 | 570 | 755 | 1135 | 1705 | 2840 | 4730 |
| 750 | 95 | 530 | 710 | 1065 | 1595 | 2660 | 4430 |
| 800 | 80 | 510 | 675 | 1015 | 1525 | 2540 | 4230 |
| 850 | 65 | 485 | 650 | 975 | 1460 | 2435 | 4060 |
| 900 | 50 | 450 | 600 | 900 | 1350 | 2245 | 3745 |
| 950 | 35 | 280 | 375 | 560 | 845 | 1405 | 2345 |
| 1000 | 20 | 165 | 220 | 330 | 495 | 825 | 1370 |
Pressure temperature rating chart for ASTM A182 Gr. F304, 304L
| Temperature °F | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -20 to 100 | 275 | 720 | 960 | 1440 | 2160 | 3600 | 6000 |
| 200 | 230 | 600 | 800 | 1200 | 1800 | 3000 | 5000 |
| 300 | 205 | 540 | 720 | 1080 | 1620 | 2700 | 4500 |
| 400 | 190 | 495 | 660 | 995 | 1490 | 2485 | 4140 |
| 500 | 170 | 465 | 620 | 930 | 1395 | 2330 | 3880 |
| 600 | 140 | 435 | 580 | 875 | 1310 | 2185 | 3640 |
| 650 | 125 | 430 | 575 | 860 | 1290 | 2150 | 3580 |
| 700 | 110 | 425 | 565 | 850 | 1275 | 2125 | 3540 |
| 750 | 95 | 415 | 555 | 830 | 1245 | 2075 | 3460 |
| 800 | 80 | 405 | 540 | 805 | 1210 | 2015 | 3360 |
| 850 | 65 | 395 | 530 | 790 | 1190 | 1980 | 3300 |
| 900 | 50 | 390 | 520 | 780 | 1165 | 1945 | 3240 |
| 950 | 35 | 380 | 510 | 765 | 1145 | 1910 | 3180 |
| 1000 | 20 | 320 | 430 | 640 | 965 | 1605 | 2675 |
| 1050 | 20 | 310 | 410 | 615 | 925 | 1545 | 2570 |
| 1100 | 20 | 255 | 345 | 515 | 770 | 1285 | 2145 |
| 1150 | 20 | 200 | 265 | 400 | 595 | 995 | 1655 |
| 1200 | 20 | 155 | 205 | 310 | 465 | 770 | 1285 |
| 1250 | 20 | 115 | 150 | 225 | 340 | 565 | 945 |
| 1300 | 20 | 85 | 115 | 170 | 255 | 430 | 715 |
| 1350 | 20 | 60 | 80 | 125 | 185 | 310 | 515 |
| 1400 | 20 | 50 | 65 | 95 | 145 | 240 | 400 |
| 1450 | 15 | 35 | 45 | 70 | 105 | 170 | 285 |
| 1500 | 10 | 25 | 35 | 55 | 80 | 135 | 230 |
Pressure temperature rating chart for ASTM A182 Gr. F316, 316L
| Temperature °F | 150# | 300# | 400# | 600# | 900# | 1500# | 2500# |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -20 to 100 | 275 | 720 | 960 | 1440 | 2160 | 3600 | 6000 |
| 200 | 235 | 620 | 825 | 1240 | 1860 | 3095 | 5160 |
| 300 | 215 | 560 | 745 | 1120 | 1680 | 2795 | 4660 |
| 400 | 195 | 515 | 685 | 1025 | 1540 | 2570 | 4280 |
| 500 | 170 | 480 | 635 | 955 | 1435 | 2390 | 3980 |
| 600 | 140 | 450 | 600 | 900 | 1355 | 2255 | 3760 |
| 650 | 125 | 445 | 590 | 890 | 1330 | 2220 | 3700 |
| 700 | 110 | 430 | 580 | 870 | 1305 | 2170 | 3620 |
| 750 | 95 | 425 | 570 | 855 | 1280 | 2135 | 3560 |
| 800 | 80 | 420 | 565 | 845 | 1265 | 2110 | 3520 |
| 850 | 65 | 420 | 555 | 835 | 1255 | 2090 | 3480 |
| 900 | 50 | 415 | 555 | 830 | 1245 | 2075 | 3460 |
| 950 | 35 | 385 | 515 | 775 | 1160 | 1930 | 3220 |
| 1000 | 20 | 350 | 465 | 700 | 1050 | 1750 | 2915 |
| 1050 | 20 | 345 | 460 | 685 | 1030 | 1720 | 2865 |
| 1100 | 20 | 305 | 405 | 610 | 915 | 1525 | 2545 |
| 1150 | 20 | 235 | 315 | 475 | 710 | 1185 | 1970 |
| 1200 | 20 | 185 | 245 | 370 | 555 | 925 | 1545 |
| 1250 | 20 | 145 | 195 | 295 | 440 | 735 | 1230 |
| 1300 | 20 | 115 | 155 | 235 | 350 | 585 | 970 |
| 1350 | 20 | 95 | 130 | 190 | 290 | 480 | 800 |
| 1400 | 20 | 75 | 100 | 150 | 225 | 380 | 630 |
| 1450 | 20 | 60 | 80 | 115 | 175 | 290 | 485 |
| 1500 | 20 | 40 | 55 | 85 | 125 | 205 | 345 |
How to Select Flange Pressure Rating for Piping System?
Flange pressure rating selection 05 step process which are:
- Determine the relevant standard to which flanges must to meet. For e.g. ASME B16.5
- Within that standard identify the correct material type to be used for some specific fluid. For e.g. ASME B16.5 has more than 30 material types.
- Determine the maximum pressure that a flange need to hold.
- Determine the maximum tempreture at which flange will operate.
- Search for the most suitable value from the chart above with respect to selected material, pressure and temperature.
For example, we will determine which class of flange will be suitable for A105 Gr. B pipe class at operating temperature 370°F and Operating pressure 426 psi. For this we have to follow the same steps as mentioned above:
- We know relevant standard of flange selection here is ASME B16.34 according to pipe class A105.
- Working pressure and temperature is know to us. i.e. 426 psi and 370°F respectivley.
- From the first table of “Pressure temperature rating chart for ASTM A105, A350 Gr. LF2 & LF6 Class 1“, working pressure is above 300°F, So, row with 400°F will be selected.
- In that row the minimum rating flange that hold 426 psi pressure is Class 300#.
- So, our selected flange class as per ASME B16.34 with considered operating pressure and temperature will Class 300#.
Formula for Flange Pressure Rating Calculation
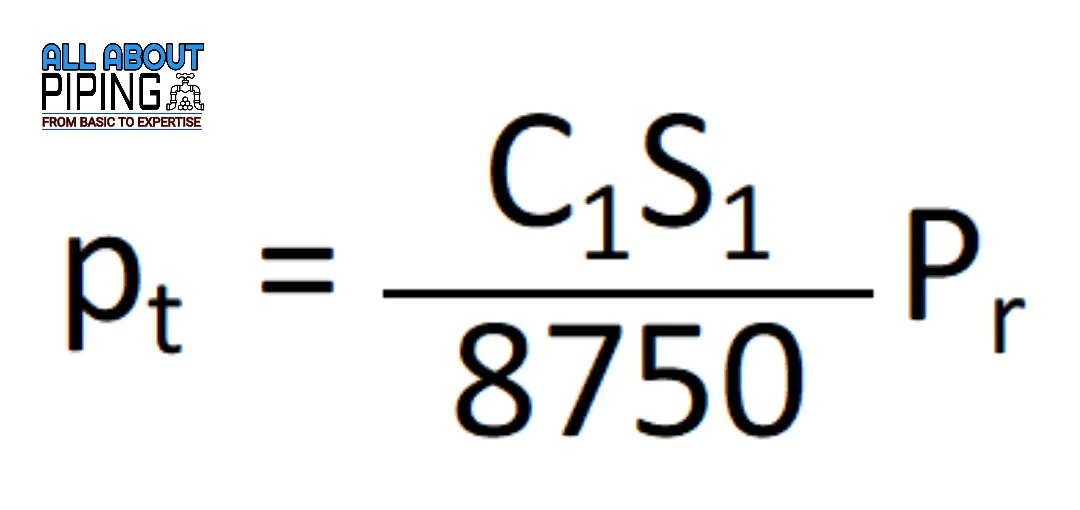
From the above image Here,
- C1 is Constant multiplying factor which is equal to 10 if S1 is in MPa and C1= 1, if S1 is expressed in psi
- Pr is pressure rating class index
- pt is oprating piping pressure for specific material at some specific temperature
- S1 is calculated stress developed on the piping system
Now if we apply the above formula for the same calculation as above:
- pt (operating pressure in psi) = 426
- S1 (stress generated on pipe because of operating pressure, in psi)= 13995 at 370°F
- C1= 1 (as stress developed is considered in psi)
So, after calculation:
Pr= (pt x 8750)/ (C1 x S1)
Pr= (426 x 8750) / (1 x 13995)
Pr= 266.345
As calculated pressure rating (Pr) is more than 150, so the preferred flange class will be 300#
Effect of Flange pressure rating on Flange size
Flange pressure rating is a technique of group making of certain pressure-temperature based ratings of flanges according to the material of flange. There are some visual effects that make a difference between a lower-class flange and a higher class flange:
- A relatively higher rating flange has respectively more thickness and can withstand more pressure and temperature.
- The outside diameter of flange will increase as flange pressure rating will increase.
- Bolt circle diameter will increase according to flange pressure rating.
- Hole size for bolt and number of bolts to install increases as flange class increases.
- Width of flange raise face also increase with higher flange rating.
For a flange with a specific nominal pipe size e.g. NPS 12, the inner diameter will never change as the flange pressure rating will increase and if the flange has a raised face, its height won’t be affected.
Conclusion
Every type of flange in terms of pressure class has its unique capability for handling pressure and temperature. A well-chosen flange is much efficient for stopping leakage through the flange joint and withstand working pressure and temperature.
Flange made of different material shows different capabilities even it belongs to the same flange pressure rating. Flange class also has an effect on the overall dimension. This article can be concluded with the following important points:
- Flange pressure rating is important to select correct flange type for different process piping operating with different temperature and pressure.
- Pressure and temperature holding capablity varies with flange class and material used for flange preparation.
- “Nominal Pressure” and “Pressure Class” are standards for flange classification. While Nominal Pressure is European standard Pressure Class is American standard for flange.
- In American standard, there is total 07 types of flange class available. i.e. 150#, 300#, 400#, 600#, 900#, 1500#, 2500#.
- In European standard many classes of flange exist. For e.g. PN6, PN10, PN16, PN25, PN40, PN63, PN100 and many more. Numerical digit after PN indicate how much pressure that flange can hold in “bar”.
- Pressure-Temperature chart is an important tabulated data that helps us to find most appropriate flange as per requirement of our piping system.
- Dimensions of flange depends on flange pressure rating.