With the Installation of the Piping system, the Installation of piping Support plays a crucial role in the stability, positioning, and movement control of pipes on their location. Different types of piping supports have different roles for the stability of the Piping system.
A properly designed and well-maintained pipe support span carries all load of the piping network and increases the life span of construction. Each piping support detail has its own importance to restrain pipe movements.
While Shoe or saddle-support helps a piping system to rest on its location, Guide and Limit stopper restrain piping movement from its location. In this article “Piping Support” we will give you a wide approach towards understanding the following:
- General classification and types of Supports
- Piping supports Standard and Codes
- Purpose of Different Types of Supports in Piping System and their installation guidance.
- Piping support arrangement in Pipe rack and Equipment
- Support Type selection and Piping Support Spacing Determination
Table of Contents
Piping support General classification
A piping system needs to be supported from some foundation or from a structure nearby. The whole weight of the Piping network is transferred to those Civil foundations or Structures. In a piping support system, some supports are directly attached to pipes while some support types are not.
Based on the attachment of Support to pipes there are two types of Support in the Piping Support System:
- Primary Supports: These types of support are directly clamped or welded to pipes for their resting. For example Shoe, Saddle, Pipe Hanger, Wear Pad, Trunnion Etc.
- Secondary Support: These are the type of support which not directly connected pipes but connected to either civil foundations or Structural members. With the help of these secondary supports, Primary support rests on its location. Antifriction Pad, Limit stopper, Guide, Goalpost are some of the examples of secondary supports.
Featured Article: Piping Supports as Per Insulation System: Hot insulated, Cold Insulated, Non-Insulated
Pipe Support types and Installation Guide
In support design, there are various types of support in piping that help pipes for their stability and poisonings. Some of the individual support or a combination of these types of support for the piping systems have their own design criteria and importance towards installation. The Types of Piping Supports are as follows:
Clamped Type Supports
Clamped type supports are defined as the support mechanism for suspended pipes either in horizontal or vertical conditions. Pipe clamps come in many variations as per the requirement of the piping system.
Installation guide for clamped supports
During installation of clamped pipe support few points to be followed are:
- The position of clamped type support can be adjusted during installation to correct any mismatch. considering no stress critical line.
- If a situation of corrosion is there, the precaution of ingress of water must be considered during installation.
- For a higher temperature range above 230ºC, a shear lug should be provided to prevent the pipe from slipping under the clamp.
- For insulated pipes, insulation thickness on clamped supports should increase to avoid any penetration on insulation cladding.
Welded Type Supports
Supports that are directly welded to pipes are defined as welded-type supports. These types of supports are less susceptible to corrosion with respect to clamped supports. As some exception in the following cases welded types supports are not advised to use:
- where post welding heat treatment is required.
- Expensive piping material like titanium, Alloy 276, Alloy 400.
- Galvanized Piping
- Piping Lined with Glass, Rubber, or Plastic
Installation guide for welded supports
- In the case of hot-dip galvanized piping, galvanization should be done after support welding.
- Supports of piping system with heat tracing should be designed such as it won’t obstruct heat tracer.
- The plane of Pipe and support should be parallel all over the piping network to maintain an equal level at each point (except for slope lines).
- Supports should be designed such as after welding actual stress should not be more than allowable stress.
- Dimension of welded support should be designed with consideration of insulation thickness.
More to Read: Heat Tracing in Piping: Types, Working, Use, Installation, Comparison
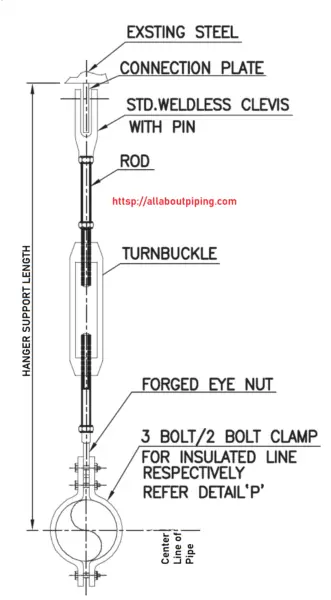
Hanger Type Supports
Pipe support in vertical position consists of rod and clamped to pipe for piping positioning is called hanger support.
Installation guide for Hanger supports
- Pipes with hanger support should be supported individually.
- Hanger supports should not be used in case of two-phase flow
- This type of support should be used where more vibration present in the piping system.
- The verticality of hanger support should match with the pipe center.
- For survivability of hanger supports in fire, Fire protection should be done.
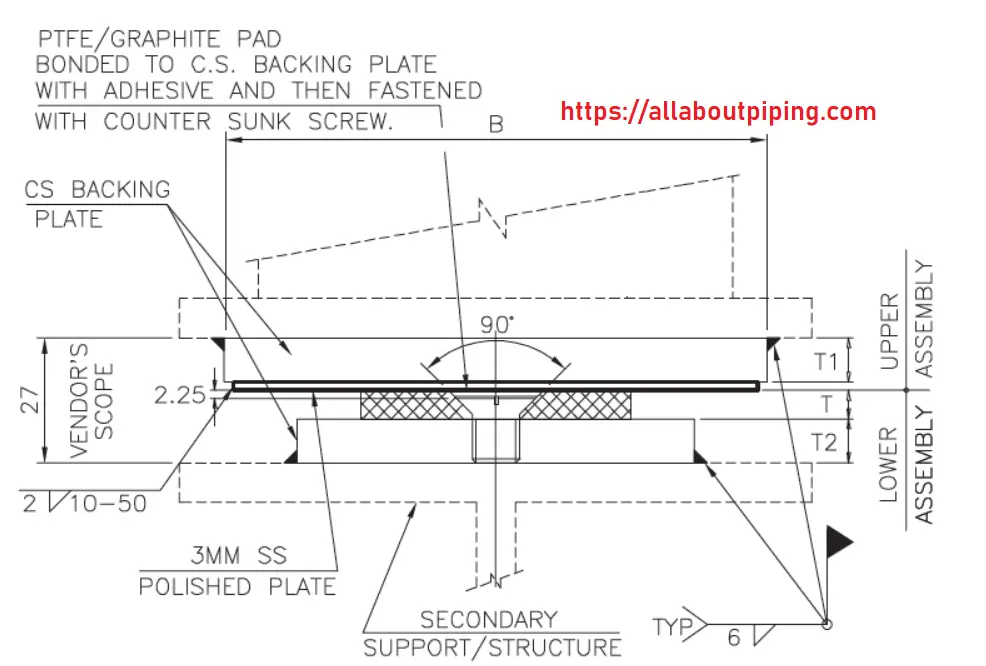
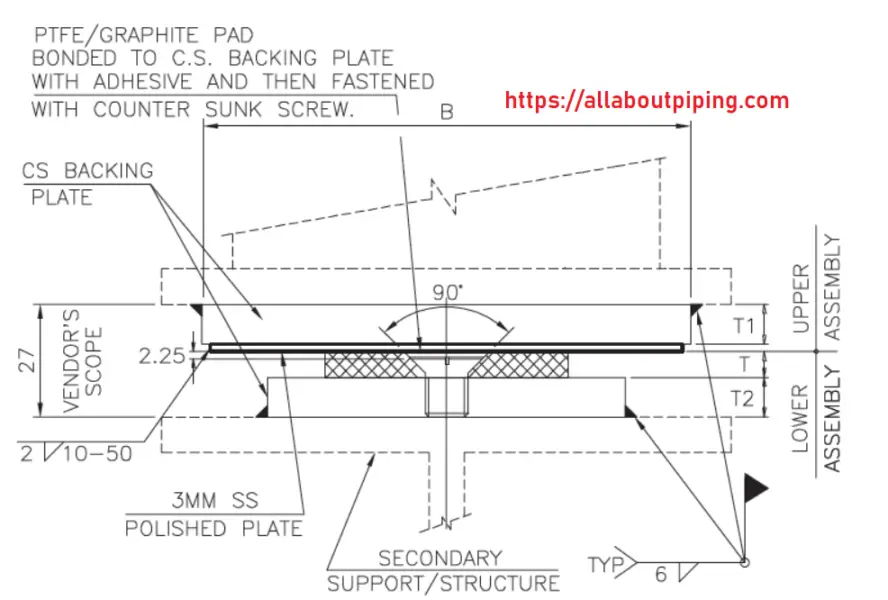
Sliding Supports
These types of piping supports are used where the vertical movement of the pipe is restrained but the horizontal movement is required. A slide support assembly is a consist of:
- PTFE or Graphite plate for a lower coefficient of friction.
- Mirror finished SS plate to reduce friction.
- CS baking plate of shoe length.
Installation guide for Sliding Support
- Mirror finished plate should be corrosion-free.
- Bonding between PTFE or Graphite plate must be good enough.
- There should be no crack in the graphite plate.
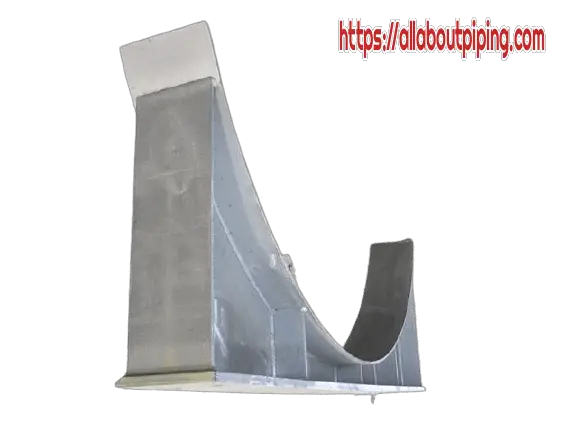
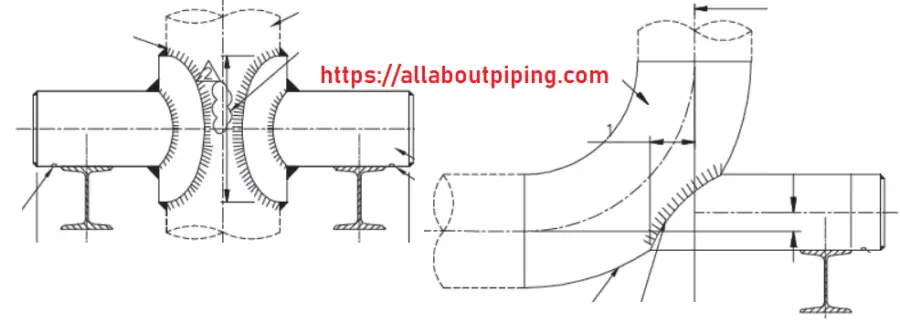
Pipe Saddles and Reinforcement pads
Saddle support is a structure consisting of a saddle and integral base that is used to support the pipe by transmitting the load or force to the adjacent structure.
Installation Guide for Pipe saddle and reinforcement pad
- Pipe saddle-support or reinforcement pad should be made from the same material as the pipe.
- Since saddle-support consumes more material. So, it is advisable to use only when it is proven to be more economical in its life span.
- Vent holes must be provided for venting out gases produced during welding and should be plug after the leak test.
- Saddle support or reinforcement pad should not be used in the piping systems with temperatures of more than 200ºC. This temperature level will create stress in welding due to the temperature difference between pipe walls and support.
- Saddle or Reinforcement pad should not be used in the corrosive environment as it is impossible to inspect pipe under saddle or reinforcement pad.
Spring Supports
A support system with a helical spring combination is considered as spring support. A manufacturer must follow MSS-SP 58 or MSS-SP 69 for the fabrication of spring or hanger support. Spring support can be of two types:
- Constant load spring Support: In constant load spring support, the load remains constant even when pipe movement is there. With the same constant load, constant spring support acts as a rigid support.
- Variable Load Spring Support: This basically consists of a spring that can get compressed or expand according to the movement of the pipe
A spring Support should be provided with a Stainless steel metal tag which should mention the following details:
- Manufacturer’s name and address
- Tag number of Spring assembly
- Spring Scale
- Cold load and hot load marking
- Spring type, Size, and Serial number.
- Manufacturing date.
Installation Guide for Spring Support
- Design of Spring support should be as per operational load of pipe.
- All parts of Spring should be hot-dip galvanized.
- Installation of spring support should be in a way Hanger rod of spring support should be in tensile load only.
- Spring locking arrangement should be broken until the line is having its operating load.
- Constant and variable type spring support should be provided with travel stop
Secondary Steel Supports
Secondary supports are a type of supports used in piping that doesn’t take a direct load of pipe but transfer all load of pipes to adjacent structural or civil members. This Support is made from steel structural members like Angle, Channel, Beam, and Plate as per support location requirement.
Installation Guide for Secondary Support
- Type Structural member must match as per the design detail.
- There should not be any space for water clogging.
- An extra stiffener plate should be added to the main structural member if secondary support is transferring load of the higher size of pipe i.e. 4″ NB of above.
- There should be any gap between secondary and primary support for complete load transfer without any jerk.
- Straightness of Structural members is mandatory to withstand the operational load.
Special Pipe Supports (SPS)
Types of piping support that not defined by a standard combination of supports and are designed to meet the piping requirements are called special pipe supports. For special pipe supports a fully detailed support fabrication drawing is produced.
Installation Guide for Special pipe Support
Since SPS are specially designed to support meet the requirement of the piping system thus installation should fulfill all requirements as per design detail.
Piping Support standards and Codes
ASME B31.3 specifies under section 321.1.1 that, layout and design of piping support elements shall be designed to fulfill the following:
- There should not be any leakage because of pipe supports.
- No excessive thrust or movement on connected equipment and structure.
- There should not be any disengagement of piping from its support.
- Designed support should withstand fluid-induced vibration.
- Thermal expansion or contraction should be considered while designing a piping support system.
- Type of pipe support should promote any heat loss or gain from the environment.
Some of the piping support standards are as follows:
- ASME 31.1 and 31.3 i.e. Power Piping and Process Piping
- MSS SP-58 Pipe Hangers and Supports – Materials, Design, and Manufacture (USA)
- MSS SP-69 ANSI/MSS Edition Pipe Hangers and Supports – Selection and Application (USA)
- MSS SP-77 Guidelines for Pipe Support Contractual Relationships (USA)
- MSS SP-89 Pipe Hangers and Supports -Fabrication and Installation Practices (USA)
- MSS SP-90 Guidelines on Terminology for Pipe Hangers and Supports (USA)
- MITI 501 for technical regulation in Japan
- BS-3974 Specification for pipe Supports in the UK
- RCC-M specification for pipe Support applicable in France
- VGB-R-510 L Standard support guideline (Germany)
Piping Support Design
Among all the various types of support Selection and designing of piping, support is elements that need to follow the rules of physics like tension, compression, vibration, shear, and stress.
A piping system needs to be well designed and adequately support. If this fails many problems like bending of flange joint, sagging of pipes, vibration, excessive movement, higher deflection, over-stress on equipment nozzle can be observed.
Let us understand some of the important points for designing a support type for any piping system:
- Objective of Designing pipe support: A well designed piping support system with proper selection of material imporve the quality of piping. This increase life span of piping network and reduces the maintenance.
- Support Tagging and Identification: All the piping support shown in piping isometric drawing should be neatly tagged with unique identification. This identification of support type can vary from organisation to organisation.
A drawing containing all those details like identification description, dimentions is know as pipe support stndard. Some of the factor is special case can’t be covered in Standard support drawing so Standard pipe support drawings are produced. - Piping Isometric: When preparing the piping isometric drawing all details including piping material, pipe support tag, pipe size, quantity and materials that would be welded on pipe need to be shown.
- Pipe Support Data: Once all details and tagging of support is done you must list out all the required support that going to be need for piping erection.
- Pipe Support Material: Among the various types of support like saddle, spring, sliding, a stress engineer need to find out a good fit for some specific piping network. Right support material always improves piping stablity in extreme weather condition .
Purpose of Standard Support in Piping
All the types of Support in piping have some unique and important functionality towards the piping system. The Various functions the Pipe support system serves are:
- Absorbs excess vibration of the piping system.
- Eliminate excess stress on pipe produced because of sagging.
- Restrain undesirable movement of pipe because of expansion or contraction.
- Transfer load of pipe and it’s component to the main structure.
- To prevent unwanted misalignment of pipes
- To prevent any load of Pipe on equipment nozzles
Determination of Pipe support location
Location of piping support is decided depending on many factors and considerations such as pipe size, Piping system configuration, Location heavy components, and availability of supporting structure. Consideration for Piping support location follows:
- Supports should not be positioned on valves, flanges, and any other piping components.
- Support should be located on the pipe as close as possible to heavy components on the piping system.
- At positions where vertical movements are minimum.
- On piping sections that don’t require removal or disconnection of support during maintenance of equipment.
- Supports should be located as close as possible to change in direction of the piping system.
- For Pipes connected to pumps, the first support of the pipe should be connected to a common civil foundation.
- For stress, critical line support location should be considered as a stress analysis outcome.
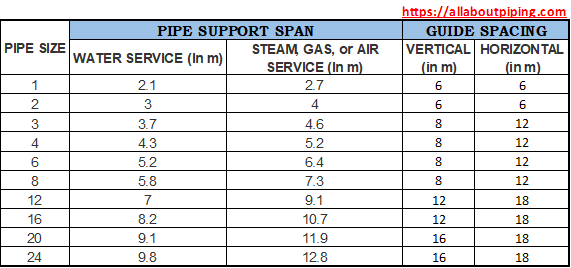
Pipe Support Span or Spacing
Distance between two support for a piping system is based on many factors like pipe size, the weight of piping components, piping material, wind speed, etc. The above image shows a general consideration pipe support span for typical piping.
Pipe Support Material selection
Pipe support material selection shall be in accordance with the following:
- All welded-type pipe supports have pipe support component materials of the same grade as the main pipe.
- Components of clamped type pipe supports that are in direct contact with the pipe are the same basic grade as the base pipe material.
- Components of clamped type pipe supports that are not in direct contact with the pipe are compatible with maximum/minimum exposure temperatures.
- All hanger-type pipe supports have clamp support material of the same basic grade as the base pipe material.
- All hanger-type pipe supports have carbon steel hanger rod attachment.
- Polymeric materials used in the construction of pipe supports are compatible with the maximum/minimum exposure temperatures.
Pipe Support Selection Guide
The basic parameters for support selection guide are as follows:
- Process design conditions
- Pipe material of construction
- Piping Loads including Piping weight, fluid,weight, Valves,inline instruments etc.
- Insulation material,thickness,density & specification.
- Piping General Arrangement drawing
- Thermal forces,moments & displacement of Piping
- Occasional loads: Hydrotest loads, Sesimic loads, wind loads etc.
Pipe Support arrangement in Pipe Rack
- For straight sections of piping in a pipe rack or pipe track > 100 m (330 ft), at least one anchor support shall be provided regardless of design temperature.
- Pipe anchor supports shall be grouped to minimize the number of anchor bays.
- Fixed axial pipe supports shall be located at the following to minimize axial movement:
- A. Process unit battery limit.
- B. Piping around pumps, compressors, and other strain-sensitive equipment.
- C. Piping near pipe rack or pipe track crossings.
- Piping systems in pipe racks or pipe tracks shall be guided at intervals of 2x the pipe support span for bare, vapor service. This is to guard against the lateral movements due to thermal expansion, including solar radiation.
- Pipe shoe supports of varying heights used on sloping lines shall be designed to withstand buckling loads.
Pipe Support for Piping system Connected to Equipment
Pipe Supports for different types of equipment acts differently which should be considered while designing of pipe support system.
Support systems connected to columns and vertical vessels
- All supports for equipment piping should be designed and selected to cope with the maximum temperature difference between the piping and the equipment.
- The piping systems should have resting support as close as possible to the column or vessel nozzle and be guided at suitable intervals to safeguard the line against wind load and/or buckling.
- Vertical pipe runs shall have a maximum guide distance as per the following: a. 6m for piping systems of size < DN 200 (NPS 8); b. 10m for piping systems of size DN 200 (NPS 8).
- Pipe supports on equipment should be of bolted type, connecting to welded cleats on the equipment.
- To support piping systems connected to equipment, maximum use should be made of platforms, table tops, and fire decks.
Piping systems connected to heat exchangers
To allow adequate clearance for the removal of covers, heads, channels, bundles, and shells, the piping system shall not be supported on heat exchanger shells and heads.
Piping systems connected to rotating equipment
- Compressor piping systems should be supported independently from a grade level in order to prevent transmission of vibrations to the compressor house.
- Piping connected to rotating equipment should have adjustable supports to facilitate alignment, spading, and equipment exchange.
- Integral (e.g., interstage) piping system of reciprocating compressors and pumps should be supported from the common foundation.
- Vibration dampener type pipe supports should be used at pipe supporting locations for piping systems connected to the reciprocating compressor to prevent the vibration forces and allow the axial thermal movements of piping, as required.
- Where lateral movements are essential, slotted holes shall be provided on the vibration dampener pipe supports.
Pipe Support System in Freezing Climate
- To avoid frost heave damage, pipe supports from grade level shall be supported by one of the following: a. foundation set on the below-frost depth; b. foundation set on grading material that is not susceptible to frost.
- Secondary pipe support materials (i.e., structural steel materials) which are not welded to the pipe shall have a minimum impact energy of 20J at the lowest ambient temperature (LAT). LAT is sometimes referred to as the lowest one-day mean ambient temperature (LODMAT).
- The material of all-welded type pipe supports, including trunnion pipe, shall be the same as the main pipe material or equivalent plate material grade.
- All clamped type pipe supports that are in contact with the pipe shall have component materials of the same basic grade as that of base pipe material.
Conclusion
Each supported type in the pipe has a vital role in the stability of the piping system. Supports are required to transfer a load of pipe and piping components to a Civil foundation or Structure. From this article, we can conclude that:
- There are generally two types of support: Primary supports and Secondary Supports.
- While some supports take a load of pipes, some support restrain pipe movements.
- There are multiple standards for support design that vary according to environmental conditions and some specific requirements of each project.
- Determination of support location is an important decision that is a result of the stress analysis outcome of a piping system.
- For any support directly attached to some equipment have different specification and roles
- Any support directly attached to any vessel or column is always having a bolting connection with the equipment.
- Support of Pipe flange connected to rotating equipment should not have any load on equipment flange.