It is very often in piping to take branch connection in piping to distribute fluid flow in multiple directions towards multiple types of equipment. Designing and Installing a single line for each piece of equipment working with the same fluid is quite complicated.
To Reduce material requirements, Design decency, and Simple piping network we used to take branch connection pipe to pipe. As per ASME B31.3 pipe to pipe branch connection chart required by the piping network is being designed for maximum optimization of the piping network.
In this article “PIPING BRANCH CONNECTION” you will find brief knowledge about:
- Branch piping Definition and Why it is being used?
- Type of Generally used Branch interconnection.
- Features of Stub branches.
- Difference between typically used branch connection.
Featured Article: Heat Tracing in Piping: Types, Working, Use, Installation, Comparison
Table of Contents
What is Branch Pipe?
Pipe connection from a mother pipe or header pipe of an equal or lesser size in any degree of rotation and orientation is called branch pipe. This branch connection is also called a tapping connection. This helps to distribute fluid from the main header pipe to different locations.
What is Branch Connection in Piping?
Taking a tapping connection from a run pipe directly by making a hole in the run pipe or using an outlet fitting is called a branch connection. This provides a connection of pipe for fluid flow from a higher diameter of the pipe to a lower diameter of the pipe.
According to the Size of the Pipe, the Fluid pressure and thickness of the Pipe reinforcement pad are required for strengthening the branch pipe. Branch connections are made onto operating pipelines, known as hot taps.
All line that connects another line to header line including drain, vent, and piping instrument connection is considered as branch connection.
Why Branch connection is required in Piping?
Making a branch connection in the run pipe or header pipe is useful in many ways to avoid complex networks. Some of the required necessities are as follows:
- Distribution of fluid up to the different columns, vessels, storage tanks, Pumps, and Exchangers.
- Reducing the cost of fittings used for taking branches from the run pipe.
- For Provision of drain and vent for hydro test purpose.
- Accumulation of fluid pumped from different pumps to generate pressure.
- For installing instrument connection on header pipe.
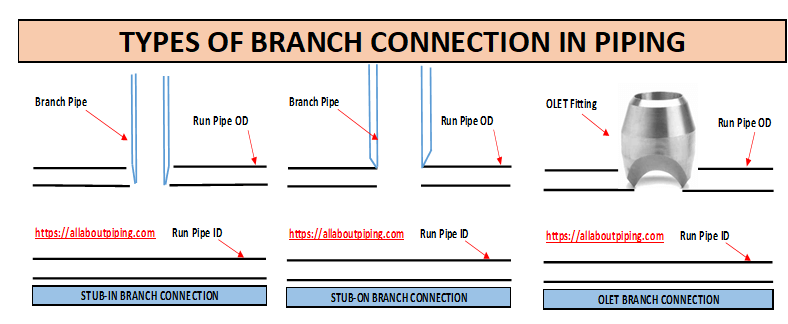
Types of Branch Connection in piping
Apart from the Standard Tee connection for taking branch pipe, there are 03 types of welded branch connection in piping standards that are followed for any piping network. Some branches or tapings are fabricated by making a hole in the run pipe and welding less diameter pipe in the same.
A fabricated branch pipe will need a reinforcement pad for providing more strength to the branch as per its design requirement.
Some Piping Branch connections use pipe fittings or specifically olet fittings for taking branches in the pipe. These olet fittings come with integrally reinforced projections that make them a more reliable and strong branch connection.
03 branch connection that is generally used in piping is as follows:
- Stub-in branch
- Stub-on branch
- Olet branch
More to Read: Piping Supports: Types, Codes, Design, Selection, Working, Installation
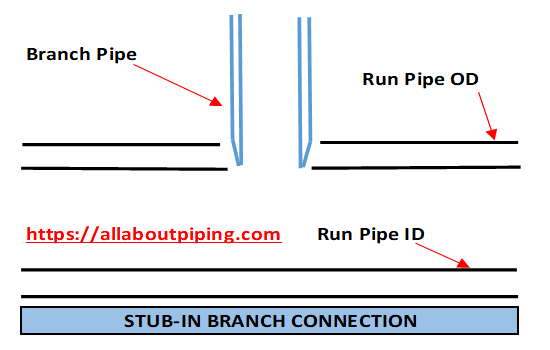
Stub-in Branch Connection
Stub-in is a type of branch from a run pipe that is fabricated by making a hole of 6mm greater than the outer diameter of the branch pipe.
In other words, A stub-in branch is fabricated by making a larger hole in the run pipe than the outer diameter of the branch pipe. In the case of a Stub-in fit-up branch connection, the Edge of the branch pipe shares the same level of Inner diameter of the header pipe.
After that, Pipe branch connection welding is done to make a connection form like a reducing tee. A Stub-in branch is generally fabricated when the Branch Pipe diameter and run pipe diameter has a difference of more than one size.
For Example; If Run pipe has a Nominal size of 12 Inches and the Branch pipe has a nominal size of 8 inches (More than one size difference) then the type of branch connection will be of Stub-in.
As per design requirements, Pipe branch connection reinforcement is done by adding a reinforcement pad made of the same material and size as run pipe. This gives the branch enough strength to sustain stress and pressure developed by Fluid flowing in the pipe.
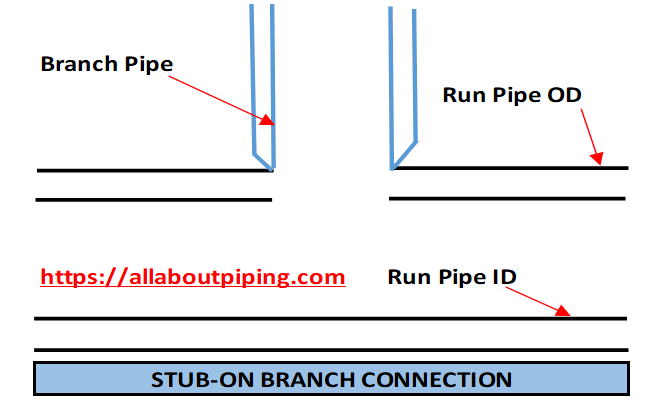
Stub-on Branch Connection
Unlike Pipe branch connection Stub-in, Stub-on is a type of branch which is fabricated by making a hole of similar size as of branch internal diameter.
In simple words, the Stub pipe connection is done by making a hole of size equal to the size of the internal diameter of the branch pipe. This branch doesn’t go inside the hole but stays on the upper surface of the run pipe only and the Stub-on pipe fit-up is done. After fit up, it will look like a branch is “seated on” Run pipe.
Stub-on Branch is fabricated when:
- Branch Pipe and Header pipe is of the Same size, or
- The difference between the Size of Run pipe and Branch pipe is not greater than that of one size.
For Example; If Run pipe is of nominal size 12 inches and the branch pipe is 12 inches too or 10 inches (Not more than one size difference) Stub-on branch fabrication will be done.
Here also Rf pad or repad is added as per design requirement for strengthening the pipe branch connection.
More Resources: Basics of Project Execution Plan for Piping Planning: A short Briefing
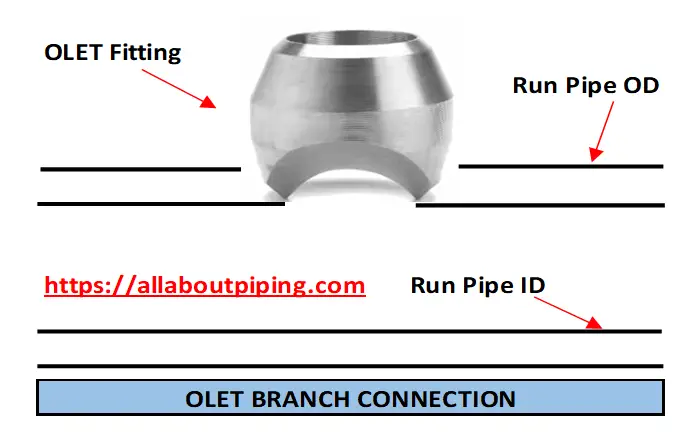
Olet Branch Connection
Olet Branch Connection done by using self-reinforced fitting or Olet fitting is termed as Olet branch connection. This type of connection either can be welded or threaded based on the olet fitting used for taking the branch outlet from the header pipe.
Olet fittings are available on different sizes of branch outlet sizes. This is basically a self-reinforced fitting that has sufficient capacity to handle stress and pressure developed in pipes.
Commonly olet fitting is used to take a branch at 90 degrees. However, some specially designed and manufactured Olet fittings are also available to make 45-degree connections.
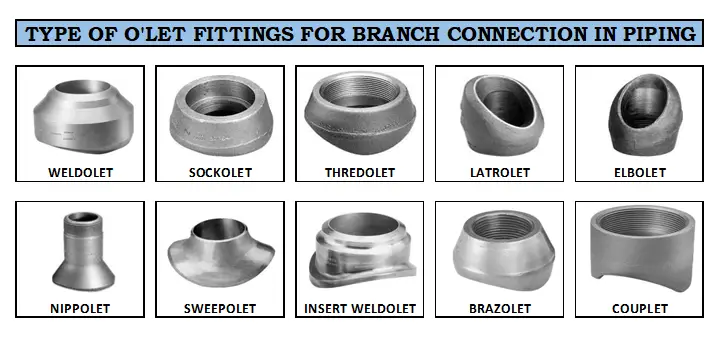
There are multiple types of Olet fittings available that are being frequently used for tapping connections from the run pipes. Types of Olets fittings frequently used are:
- Sockolet: These Olet fittings is reinforced branch fitting socket weld branch connection from the run pipe. this manufactured in 3000#, 6000#, and 9000# pressure rating.
- Weldolet: The most commonly used olet fitting that gives a butt-weld branch connection from the run pipe. The ends of this lot fitting are pre-beveled for taking butt weld connection.
- Thredolet: As the name specified this reinforced fitting threaded olet connection is being used where a threaded branch outlet required.
- Laterolet: This specially designed olet fits to take 45-degree branch outlet.
- Elbowlet: This is used by making holes on an elbow to take connections for instruments. This is also available with socket and threaded connection end. This is akind of self reinforced fitting on elbow connection.
- Nippolet: This is one piece fitting for valve connection take-offs, drains, vents. Nippolet is available with male thread connection or male sockets.
- Sweepolet: This olet fitting is an integrally reinforced, butt-weld branch connection olet with low stress factor and long fatigue life. Weld joint to this can be easily examined with radiography, Ultrasound.
- Insert Weldolet: Like the sweepolet this has also a butt weld connection but this inserted up to the internal diameter of the pipe to take fit-up and welding connection.
- Brazolet: This is used to take branches in brass or copper tubing. Its branch connection is available in socket and thread connection both.
- Couplet: This designed for a fire protection sprinkler system for installation of QBD (Quartzoid Bulb Detector).
Features of Stub-in or Stub-on Branch Connection
Some of the features of Stub-in or Stub-on type branch connections are as follows:
- This reduces the cost of fittings required for taking branch.
- A reinforcement pad can be added to strengthen the Pipe to pipe branches.
- This saves installation time as we have to do only one weld instead of 03 weld connections as in the case of “TEE”.
- The welding Strength of the Stub-in has the same strength as of butt-weld joints. While stub-on weld strength has lower values.
- With this, we can take branches other than 90 degrees too.
Difference between Stub-in and Stub-on Branch connection
The basic difference between Stub-in and Stub-on branch type is as follows:
Stub-in vs Stub-on branch connection
| SL. NO. | STUB IN BRANCH CONNECTION | STUB ON BRANCH CONNECTION |
|---|---|---|
| 01 | Applicable when Header to Braanch Pipe size has difference more than one size | Applicable when Header to branch pipe size are either equal or has one size difference |
| 02 | Branch to Header pipe welding will be of Butt-weld type | Branch to Header pipe welding will be of Fillet weld type |
| 03 | Comparatively can handle more pressure and stress | Have less pressure and stress handling capability |
| 04 | Branch Edge matches with Internal diameter of Run pipe | Branch edge lies on Outer diameter of Run pipe |
| 05 | Have comparatively more weld strength value | Comparatively have less weld strength value |
Stub Piping Branch vs Olet Piping Branch
A branch fabricated with a pipe is called a stub and Branches fabricated with Olet fittings are called an Olet branch. The main highlighted difference between Stub Branch and Olet branch is as follows:
Olet vs Stub branch connection
| SL. NO. | STUB BRANCH CONNECTION | OLET BRANCH CONNECTION |
|---|---|---|
| 01 | this is Pipe to pipe branch connection | This is pipe to fitting connection |
| 02 | Requires Reinforcement pad for strengthning the branch connection | Self-reinforced OLET fittings does't require RF pad |
| 03 | Can't sustain with high pressure lines | Can handle high pressure |
| 04 | Comparatively less welding required | Comparatively more welding required to weld Olet to Pipe |
| 05 | Less cost comparatively for taking branch connection | More costly |
| 06 | Brach to header welding can fillet or butt type as per Stub-in or Stub-on brach connection | Branch to header will be always butt weld |
Piping Branch Connection chart
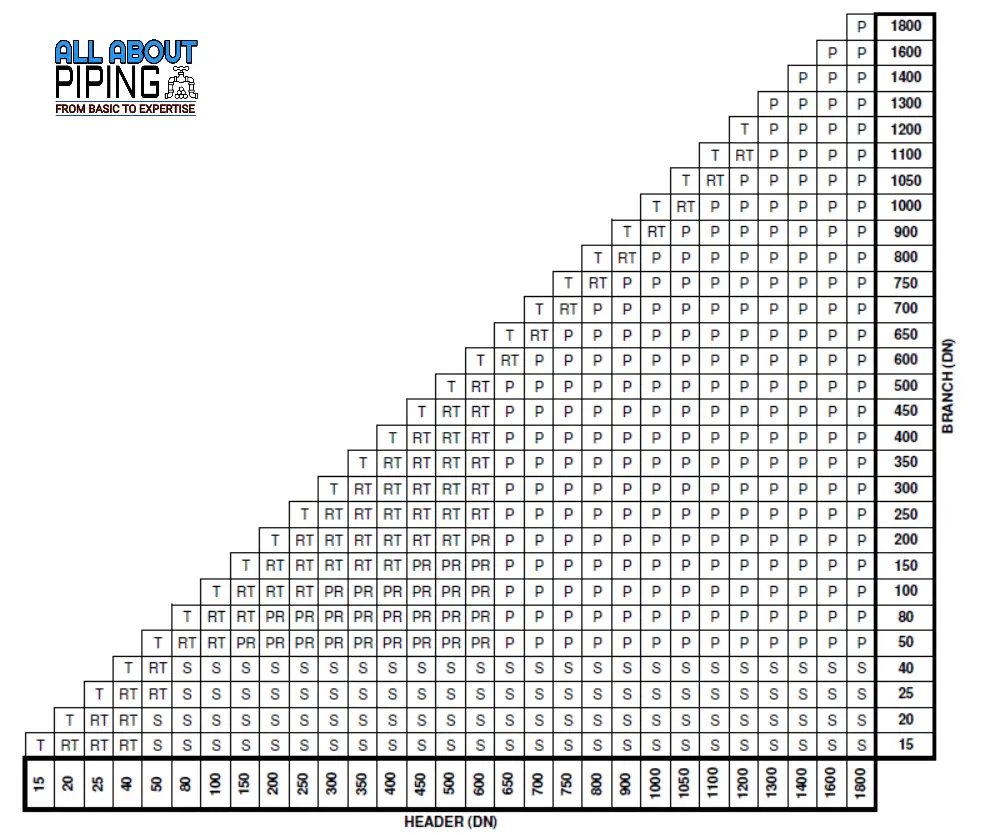
In the above image of the piping branch connection chart, there is a typically used piping branch connection chart that helps a fabricator to choose the type of connection from mother pipe to branch pipe. From the image few things to note are:
- All dimensions shown here are in “mm”
- Abbreviations used are:
- T: Connection from Equal Tee fittings.
- S: connection from a sockolet.
- W: Connection from a weldolet.
- RT: connection with reducing tee.
- P: pipe to pipe branch connection without RF pad.
- PR: pipe to pipe branch connection with RF pad.
Conclusion
A branch in Piping is much used for flow distribution, instrument installation, and providing a high point vent or Low point drain. A branch can be fabricated in 02 ways:
- Pipe to pipe Branch connection
- Pipe to fitting branch connection
In the type of Pipe to Pipe Branch connection, there are two categories:
- Stub-in branch: For Run pipe to branch pipe Size difference of more than one size.
- Stub-on branch: For equal Run and Branch or Having a difference of only one size.
Some highlighted points are as follows:
- A branch connection taken from Olet fittings is called Olet branch.
- Stub-in type branch has more pressure and stress handling capability than Stub-on branch.
- Olet fittings are self-reinforced fitting. So, they don’t require an additional RF pad why Stub-in pr Stub-on branch connection requires a reinforcement pad for strengthening branch connection.
- There are multiple types of olet fittings for different branch-type connections from the run pipe.
- Olet type branch connections are more costly than Stub branching if Rf pad is not used.